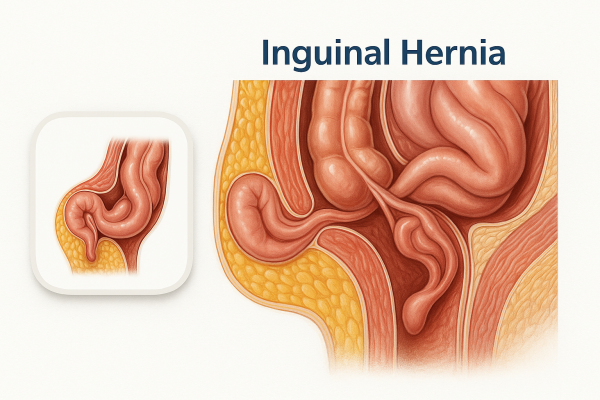
What is an Inguinal Hernia?
An inguinal hernia occurs when part of the intestine or abdominal fat protrudes through a weak spot in the lower abdominal wall, specifically in the inguinal canal (the area between the abdomen and the thigh).
It is the most common type of hernia, and it occurs more frequently in men than in women.
Types of Inguinal Hernia
There are two main types of inguinal hernia:
1. Indirect Inguinal Hernia:
Caused by a natural opening that fails to close after birth.
Commonly seen in children and young adults.
2. Direct Inguinal Hernia:
Occurs due to weakening of the abdominal muscles with age.
More common in adults, especially elderly patients.
Causes of Inguinal Hernia
Congenital weakness in the abdominal wall.
Aging and muscle weakness.
Increased intra-abdominal pressure due to:
Heavy lifting
Obesity
Chronic coughing
Chronic constipation
Pregnancy
Urinary retention
Symptoms of Inguinal Hernia
Visible bulge or swelling in the groin or lower abdomen, which may become more noticeable when standing or coughing.
Pain or heaviness in the affected area.
In complicated cases:
Sudden, severe pain
Irreducible swelling (the bulge cannot be pushed back in)
Nausea or vomiting (a sign of hernia incarceration, which is a medical emergency)
Diagnosis
Clinical examination is the primary method of diagnosis. The doctor observes the bulge, especially when the patient is standing or coughing.
Ultrasound (sonography): To assess the contents of the hernia.
In some cases, a CT scan may be requested for a more detailed evaluation.
Treatment of Inguinal Hernia
Surgical Repair:
Surgery is the best treatment option for most cases. It aims to:
Return the hernia contents to their proper place.
Reinforce the abdominal wall with a surgical mesh to reduce the risk of recurrence.
Surgical Approaches:
Open surgery (traditional method)
Laparoscopic surgery (minimally invasive, less pain, and faster recovery)
Postoperative Care:
Avoid heavy lifting for at least 4–6 weeks.
Light walking promotes faster recovery.
Maintain a healthy weight.
Eat a fiber-rich diet to prevent constipation.
Follow your doctor’s instructions and monitor the surgical site.
Need Help?
If you are experiencing symptoms of an inguinal hernia or would like to know the best treatment for your condition, don’t hesitate to visit our clinic.
Our medical team is ready to provide you with expert evaluation and care.